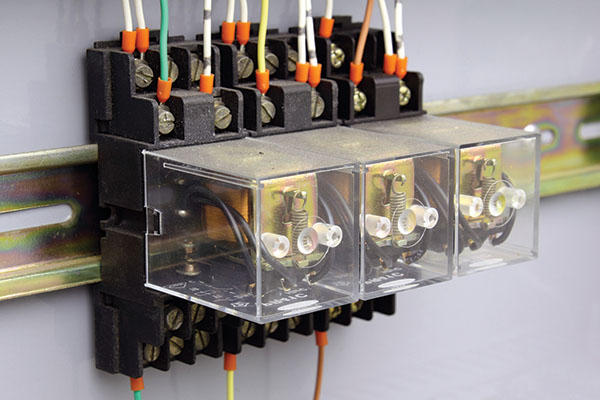
Exploring the Diverse World of Electrical Relays: Unveiling the Many Types and Applications
In the vast realm of electrical engineering, relays play a crucial role in controlling and protecting various electrical circuits. These devices act as switches, allowing the flow of current to be controlled based on specific conditions. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of electrical relays, exploring the different types and their applications.
- Electromechanical Relays:
Electromechanical relays are the most common type, consisting of a coil, armature, and contacts. When a current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, closing the contacts and completing the circuit. These relays are widely used in industrial automation, power systems, and control panels. - Solid-State Relays (SSRs):
Unlike electromechanical relays, SSRs do not have any moving parts. They utilize semiconductor devices, such as thyristors or transistors, to switch the current. SSRs offer advantages like faster switching speeds, longer lifespan, and silent operation. They find applications in areas where high switching frequencies, low power consumption, and minimal electromagnetic interference are required. - Reed Relays:
Reed relays are compact and highly reliable. They consist of two metal reeds enclosed within a glass tube filled with inert gas. When a magnetic field is applied, the reeds come into contact, completing the circuit. Reed relays are commonly used in telecommunications, test equipment, and medical devices due to their fast response time and low power consumption. - Time Delay Relays:
Time delay relays are designed to introduce a delay in the switching operation. They are used in applications where a specific time delay is required, such as motor control, lighting systems, and HVAC equipment. These relays can be electromechanical or solid-state, offering precise timing functions to ensure proper sequencing of operations. - Protective Relays:
Protective relays are crucial for safeguarding electrical systems from faults and abnormalities. They continuously monitor parameters like voltage, current, frequency, and temperature to detect any deviations from normal conditions. Protective relays are extensively used in power distribution networks, substations, and industrial plants to prevent equipment damage and ensure system reliability.
Conclusion:
Electrical relays are indispensable components in various industries, enabling efficient control and protection of electrical circuits. From electromechanical relays to solid-state relays, reed relays, time delay relays, and protective relays, each type serves specific purposes and offers unique advantages. Understanding the different types of relays and their applications is essential for electrical engineers and technicians working in diverse fields. By harnessing the power of relays, we can achieve precise control, enhanced safety, and optimal performance in electrical systems.